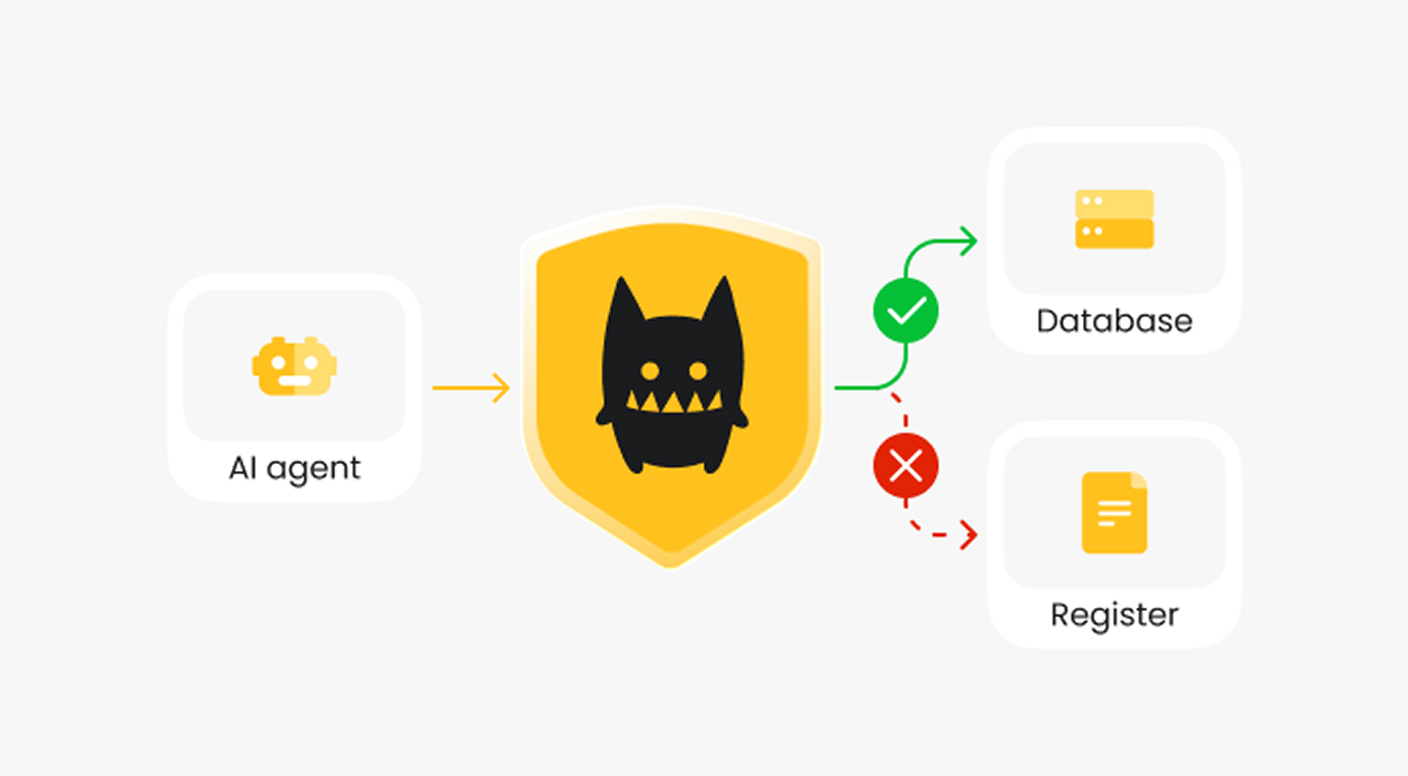
Your AI agents are making access decisions. Who controls them?
Cerbos is a deterministic authorization engine that evaluates access policies for AI agents, non-human identities, and human users in a single policy decision. Without it, every agent is an uncontrolled access path into your systems.
Agents break every assumption your identity stack was built on
They break all of them. Traditional IAM assumes human actors with bounded intent. Agents run continuously, spawn sub-agents, chain tools, and operate across multiple systems with no single choke point. Without four capabilities working together, every agent is an uncontrolled blast radius.
1
Discovery & inventory
Enumerate agents, NHIs, MCP servers, and secrets. Map ownership and relationships across the identity graph.
2
Authorization & policy
Decompose agent intent into least-privilege permission blueprints. Evaluate each request against deterministic policy.
Cerbos
3
Credential brokering
Mint short-lived, task-scoped credentials. Inject them at runtime without exposing secrets to agent code.
4
Runtime enforcement
Monitor behavioral drift. Revoke access immediately when agent activity deviates from the authorized baseline.
Cerbos
LLMs cannot make enforcement decisions
When an agent decides to delete data, escalate privileges, or access sensitive records, that decision cannot be left to a probabilistic model. Authorization decisions must be deterministic, auditable, and explainable after the fact.
Deterministic evaluation
Authorization decisions are computed against versioned policy, not inferred by a language model. Every decision is binary, auditable, and traceable to a specific policy version.
Sub-millisecond latency
Agents operating at machine speed require a policy engine that does not introduce meaningful latency. Cerbos evaluates policies in under a millisecond.
Policy as code
YAML-based policies that security teams can read, audit, and version-control. Every decision traces back to a specific policy version.
Multi-signal evaluation
Policies evaluate agent identity, delegating user context, resource attributes, action type, and environmental conditions in a single request.
When something goes wrong, who is accountable?
Nobody, unless every decision is attributable. When an agent acts on behalf of a user, accountability blurs across the user, the agent runtime, and the downstream service. Cerbos evaluates both identities, the target resource, and the current context in a single policy decision.
Agent + user composite principals
Cerbos evaluates policies where the principal includes both the agent identity and the human context it acts on behalf of. The policy sees the full delegation chain.
Attribute-based access control
Policies incorporate attributes from the agent, the delegating user, the target resource, and the environment. RBAC, ABAC, and PBAC rules compose in a single evaluation.
Contextual constraints
Time-bounded access, environment restrictions, and risk signals are first-class policy conditions. The same agent receives different permissions based on runtime context.
Agents inherit full user privileges unless you stop them
By default, they do. Without fine-grained policy evaluation, agents get all-or-nothing access, maximizing utility but creating unacceptable blast radius. Cerbos evaluates each action against least-privilege policy before credentials are issued.
Sits after intent decomposition
Orchestration layers decompose high-level agent intent into concrete action sets. Cerbos evaluates whether each action is permitted given the current principal, resource, and context.
Evaluated before credential issuance
The policy decision occurs before credentials are minted. If Cerbos denies the request, no credential is issued and no access is granted.
Least-privilege enforcement
Each permission blueprint is evaluated against fine-grained policy. Agents receive only the permissions required for the current task, not a superset of capabilities.
Static credentials are time bombs in agentic systems
Long-lived API keys, orphaned tokens, and shared secrets persist long after the business need changes. When credentials are ephemeral and task-scoped, the policy engine evaluating each request becomes the critical control point.
Per-request evaluation
Every access attempt is evaluated independently. There are no cached grants or standing entitlements. Each request carries the full context required for a policy decision.
Ephemeral credential compatibility
Cerbos operates in ZSP architectures where credentials are task-scoped and short-lived. The policy engine evaluates each request regardless of how the credential was issued.
Distributed enforcement
Cerbos Hub pushes policy updates across all PDP instances in real time. A policy change propagates to every enforcement point without redeployment.
Audit trail per decision
Every allow and deny decision is logged with the policy version, principal attributes, resource, and action. The audit trail is complete and machine-readable.
When an agent goes rogue, how fast can you shut it down?
Immediately, with a single policy update. Behavioral drift is not a hypothetical. When an agent's actions deviate from its authorized baseline, waiting for credential rotation or service restarts is not an option. A policy update in Cerbos Hub takes effect on the next authorization check.
1
Detect behavioral drift
Runtime monitoring identifies that an agent's actions deviate from the authorized baseline or approved intent.
2
Update policy in Cerbos Hub
A policy change denying access for the agent is committed. Cerbos Hub distributes the updated policy to all PDP instances.
3
Enforce immediately
The next authorization check for that agent returns DENY. No credential rotation required. No service restart. Access is revoked at the policy layer.
Purpose-built authorization, not a generic policy engine
General-purpose policy engines require teams to implement authorization semantics independently. Cerbos provides an opinionated authorization engine with first-class support for principals, resources, actions, and contextual attributes.
Generic policy engines
Policy language
General-purpose policy languages designed for broader use cases
Authorization model
Authorization patterns must be assembled from generic primitives
Evaluation latency
Varies by policy complexity and engine architecture
Policy lifecycle
Custom sync, manual distribution, separate CI/CD tooling
Audit & compliance
Decision logs require additional infrastructure to capture and correlate
Cerbos
Policy language
YAML policies purpose-built for authorization, readable by security teams
Authorization model
First-class RBAC, ABAC, and PBAC with principal/resource/action semantics
Evaluation latency
Sub-millisecond, optimized for per-request evaluation at machine speed
Policy lifecycle
Cerbos Hub: managed policy lifecycle with CI/CD, testing, and real-time distribution
Audit & compliance
Structured decision logs with policy version lineage, built in
Standards-based authorization
Cerbos implements open standards so that authorization decisions interoperate with the broader identity and security stack without proprietary lock-in.
AuthZEN
Cerbos implements the OpenID AuthZEN specification for standardized authorization API interoperability. Any system that speaks AuthZEN can consume Cerbos decisions.
SPIFFE
Cerbos integrates with SPIFFE-based workload identity. Agents and services authenticate with SPIFFE IDs, and Cerbos evaluates authorization policy against verified workload identities.
Policy as code
YAML-based policies stored in version control. Standard CI/CD workflows apply. Policies are testable, reviewable, and auditable using existing engineering practices.
Cerbos is the authorization layer your identity stack is missing
Identity platforms handle discovery, credential brokering, and runtime monitoring, but none of them make the authorization decision. Cerbos fills that gap across the entire agentic identity architecture.
Discovery & inventory
Agent discovery platforms
Discovery platforms enumerate and fingerprint agents across cloud, SaaS, and AI environments. Cerbos enforces the authorization policies that govern what discovered agents can access.
Intent translation & lifecycle
NHI management platforms
NHI platforms decompose agent intent and manage non-human identity lifecycle. Cerbos provides the deterministic policy evaluation that sits between intent translation and credential issuance.
Credential brokering
Credential brokers
Credential brokers handle workload identity and inject short-lived, task-scoped credentials at runtime. Cerbos evaluates the authorization decision before credentials are issued.
Risk-based enforcement
Step-up authentication
Step-up authentication platforms provide risk-based controls for high-risk agent actions. Cerbos evaluates the base authorization policy; step-up adds human-in-the-loop approval when required.
Authorization in production



“We rely on Cerbos to make authorization decisions across the whole mesh - millions of times a day. And it’s fast. We don’t even think about it anymore. It just works.”

Rob Crowe
Principal Engineer @Utility Warehouse
Months of dev time reclaimed by replacing scattered access logic with Cerbos PDP.
Eliminated technical debt from authorization.
Frequently asked questions
What is agentic authorization?
Agentic authorization is the process of evaluating whether an AI agent is permitted to perform a specific action on a specific resource, given the agent's identity, the delegating user's context, and runtime conditions. Unlike traditional authorization, it must handle composite identities, machine-speed requests, and non-deterministic actor behavior.
How does Cerbos authorize AI agents?
Cerbos evaluates every agent action against YAML-based policies that consider the agent identity, the delegating user, the target resource, the action being attempted, and contextual attributes like time and environment. Decisions are deterministic, sub-millisecond, and logged with full policy lineage.
What is zero standing privilege for AI agents?
Zero standing privilege (ZSP) means agents operate with no persistent access rights. Every action requires a fresh authorization decision, and credentials are task-scoped and short-lived. Cerbos enforces ZSP by evaluating each request independently with no cached grants or standing entitlements.
How do you revoke AI agent access in real time?
A policy update in Cerbos Hub propagates to all policy decision points in real time. The next authorization check for that agent returns DENY. No credential rotation, service restart, or redeployment is required.
How is Cerbos different from OPA for agentic authorization?
OPA is a general-purpose policy engine that requires teams to build authorization semantics from primitives. Cerbos is purpose-built for authorization with first-class support for principals, resources, actions, RBAC, ABAC, and contextual attributes. Policies are YAML-based and readable by security teams without specialized training.
Related resources

Ebook
Securing AI agents and non-human identities in enterprises

Webinar
Securing agentic AI in production

Ebook
Zero Trust for AI: Securing MCP Servers
Article
Implementing authorization in RAG-based AI systems with Cerbos

Article
MCP security & AI agent authorization

Article
MCP permissions: securing AI agent access to tools
Build AI systems that are safe, compliant, and trustworthy
Enforce Zero Trust and least privilege across RAG, agents, tools and data retrieval with Cerbos.

Authorization for AI systems
By industry
By business requirement
Useful links
What is Cerbos?
Cerbos is an end-to-end enterprise authorization software for Zero Trust environments and AI-powered systems. It enforces fine-grained, contextual, and continuous authorization across apps, APIs, AI agents, MCP servers, services, and workloads.
Cerbos consists of an open-source Policy Decision Point, Enforcement Point integrations, and a centrally managed Policy Administration Plane (Cerbos Hub) that coordinates unified policy-based authorization across your architecture. Enforce least privilege & maintain full visibility into access decisions with Cerbos authorization.