Cerbos PDP and Cerbos Hub: Choosing the right setup for your team
Authorization is more than a simple access check. The real operational cost comes from everything around the decision engine, such as writing policies, testing changes, distributing updates, tracking versions, and maintaining audit trails. The open source Cerbos PDP gives teams a strong and reliable authorization engine, but building the surrounding tooling yourself requires ongoing engineering effort.
Anyone who has built internal authorization tooling knows that the hardest part is never the allow or deny decision. It is everything that needs to exist around it.
Cerbos Hub provides this missing infrastructure out of the box. It gives teams a managed environment for authoring, testing, deploying, and auditing policies without building or maintaining internal tooling. This guide explains how the two options compare and when it makes sense to use the PDP alone or combine it with Cerbos Hub.
Before we dive into the comparison, let’s briefly look at what Cerbos is and how it works.
Table of contents
- What is Cerbos?
- From PDP to Hub: managing authorization at scale
- Key learnings: what should you choose?
What is Cerbos?
Cerbos enforces fine-grained access control for applications, APIs, workloads, and AI agents, ensuring every access decision meets your security and compliance requirements. Cerbos is an enterprise-grade authorization software built to secure access across complex, distributed environments, SaaS products, and regulated systems. It externalizes authorization logic from application code, making access control consistent and centrally managed across all your services.
Designed for Zero Trust architectures and AI-driven systems, Cerbos provides continuous, policy based authorization that scales from local deployments to global production systems. It supports multiple access control models, including RBAC, ABAC, and PBAC, giving engineering and security teams flexibility to model permissions the way their business needs them.
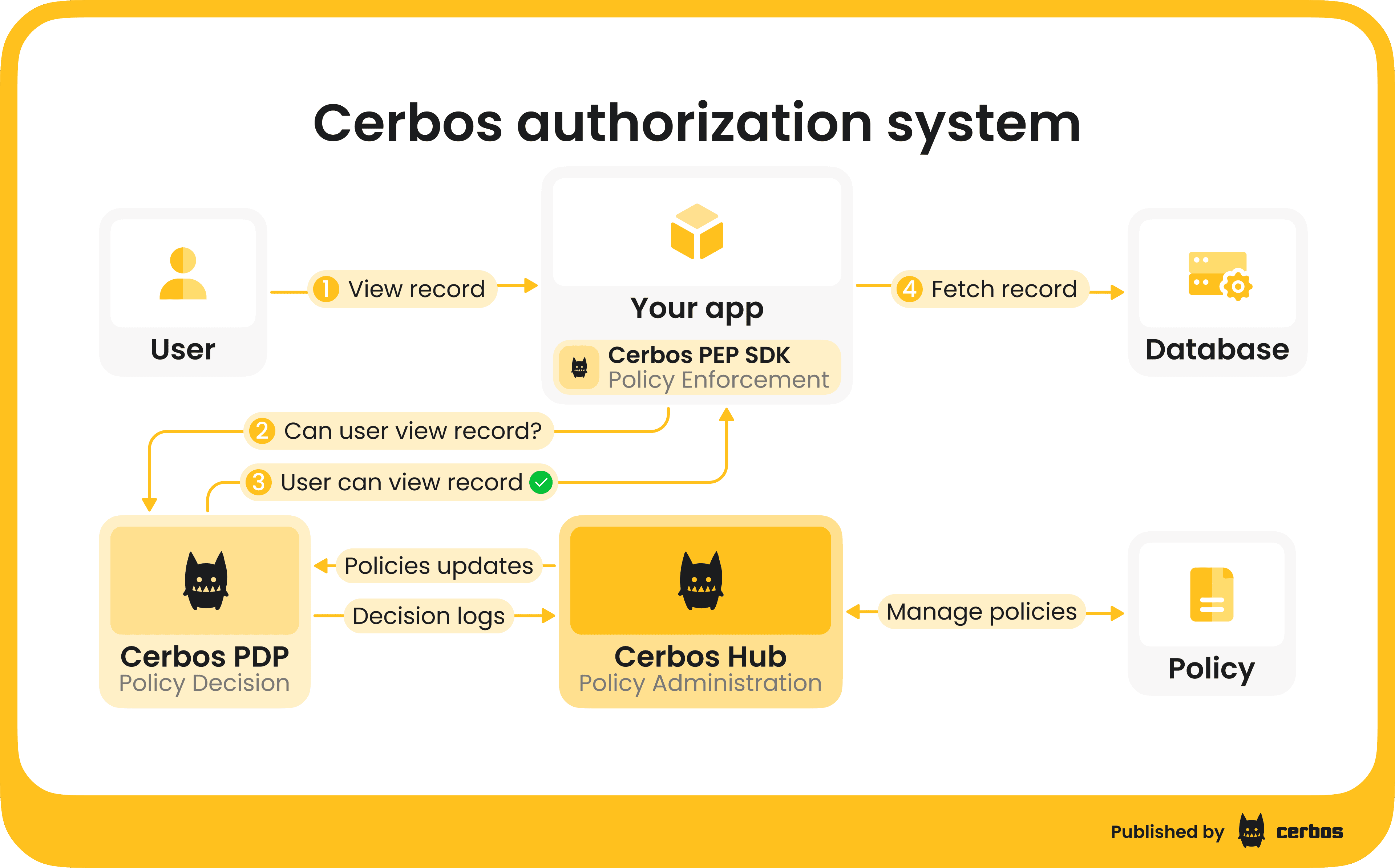
Cerbos also helps you enforce least privilege at scale and maintain full visibility into every access decision with detailed audit logs. If you want to learn more about the architecture, Cerbos’ authorization system consists of three connected components:
-
Policy Decision Point (PDP) is the authorization engine that evaluates access control logic and returns allow or deny decisions to client services. It is open source, stateless, and lightweight, which means it can run anywhere: in containers, Kubernetes clusters, or at the edge. The PDP is optimized for performance and reliability, capable of handling millions of authorization checks per second with predictable latency.
-
Enforcement Point SDKs are lightweight libraries that enforce authorization decisions directly within your applications and APIs. They provide a simple, language-agnostic interface for calling the PDP in real time and applying its allow or deny responses. The SDKs are easy to integrate and work with any identity provider.
-
Policy Administration Point (Cerbos Hub) is an authorization management software for authoring, testing, deploying, and auditing authorization policies at scale.
PDP, SDKs, and Cerbos Hub are parts of the same product and are designed to work together as one authorization system. If you want to understand the full architecture in more detail, this video from our CPO, Alex Olivier, is a helpful walkthrough:
From PDP to Hub: managing authorization at scale
Cerbos launched in 2021 with an open source PDP that gave developers a high-performance authorization engine for fine-grained access control. As teams started using Cerbos in more complex systems, they asked for an easier way to manage policies, roll out updates, and see what access decisions their services were making.
Cerbos Hub was created in direct response to those needs. It extends the open source PDP with centralized policy management, integrated testing, rollout automation, and full visibility into authorization activity across environments. As our co-founder and Head of Product explained:

Cerbos Hub centralizes these capabilities in one place. It gives teams a single control plane for operating authorization across all environments. Now let’s see how this maps to each part of the authorization workflow.
Writing access control policies
Policies are defined in YAML, a structured text format commonly used for configuration manifests. Each policy describes who can perform specific actions on given resources, using roles, attributes, and contextual conditions.
With Cerbos PDP
Cerbos PDP comes with tooling that can be run to compile and test policies on the developer's local environment. Policies can be manually validated, and IDEs can provide autocomplete using a schema. Collaborating on policies requires sharing the files with another developer directly and iterating in tandem, typically using something like GitHub to version and share changes.
When several developers or security engineers work on policies at the same time, they have to coordinate reviews manually in Git. This slows down iteration and increases the chance of merge conflicts or inconsistent updates.
With Cerbos Hub
You get the additional tooling that makes policy creation much faster and safer. You can write, test, and review policies directly in the browser-based, multi-user-editing-friendly Playground. Playground gives you instant feedback on every change, shows how rules evaluate in real time, and lets you simulate API calls or connect to a local PDP to test against your own setup.
It’s a safe environment to experiment with policies without any risks to your actual systems or data. You can also create separate playgrounds for different services or branches and share links for review. Cerbos Playground includes many more useful features:
- Pre-built examples for common application permission models
- A policy wizard for quickly generating RBAC policies
- Ability to collaborate on policies with product managers and other developers through shared playground links and real-time editing.
You can take a look at how it works in action:
Testing policies
With Cerbos PDP
You run policy tests on your local machine or in your CI environment. It works, but it takes time to maintain. You can set up your own testing pipeline with GitHub Actions, CircleCI, or another tool, but that means writing scripts, configuring runners, and managing outputs yourself. Sharing results with teammates is not simple, and finding the cause of a failed test often means combing through logs.
The PDP itself is optimized for making fast and reliable access decisions. Everything around it, including testing, validation, and deployment, is something you will need to build and maintain yourself. You can definitely spend time on these tasks, but that is time stolen from your product development.
Debugging policies is part of the job, but without shared tooling, it often takes longer than it should and it really does not need to 😄.
With Cerbos Hub
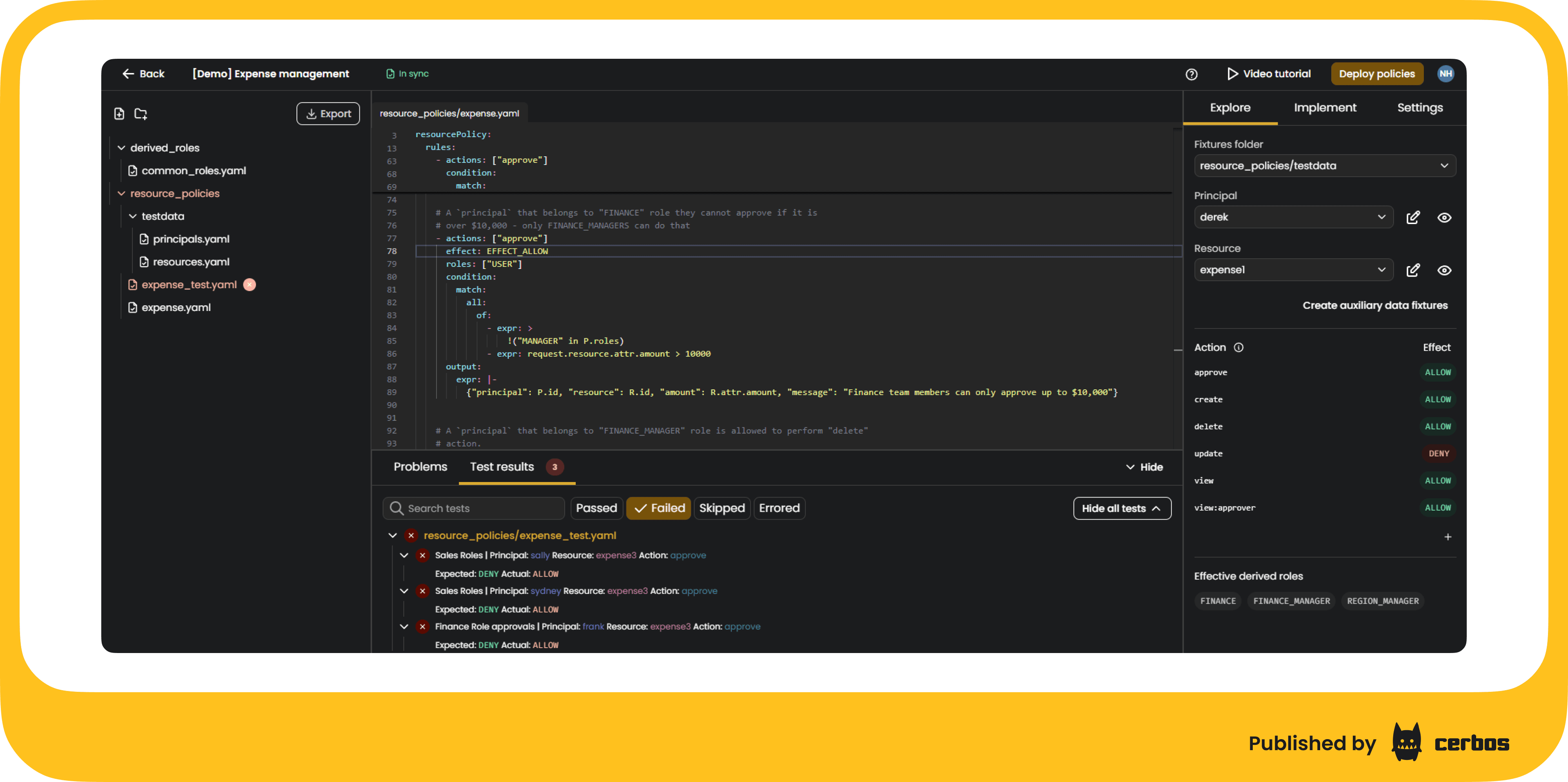
Testing is built into the workflow from the start. As I mentioned above, you can also test policies interactively in Playground as you write and edit them. Once policies are ready to move forward, Cerbos Hub takes testing a step further. It runs automated tests in a managed CI pipeline that validates policies before they are deployed. Each commit triggers compilation and verification, and results are presented in a clear dashboard showing which tests failed and why.
Hub-generated policy bundles are optimized for consistent performance across PDPs, and every test result is linked to the exact policy commit that produced it.
Cerbos Hub integrates with existing Git and CI/CD setups so you can treat authorization policies the same way you handle application code. Every change is versioned, validated, and deployed through your preferred pipeline. Policy rollouts follow your GitOps workflow, allowing deployments based on branches, tags, or specific commits. This workflow makes authorization testing consistent, reliable, and developer-friendly.
Policies distribution
With Cerbos PDP
When you use only the PDP, each PDP instance pulls its own policies. The PDP follows a pull model: every instance checks your policy store or repository at startup or on a defined refresh interval to download the latest policy bundle. This setup works, but it often creates short delays before updates reach all instances because each PDP checks for changes independently.
If you have one PDP instance and infrequent policy updates, a pull model is simple and reliable. You can even increase the refresh frequency, but that adds load on your policy store or Git repository and can create rate-limit issues in large, distributed environments.
You also need to build tooling to track which PDP has pulled the latest bundle, detect stale versions, and keep policy versions consistent across environments. This approach is fine for early-stage products or systems that do not have strict latency or compliance requirements. However, in distributed or enterprise setups, managing policy synchronization manually becomes harder as you scale.
With Cerbos Hub
Cerbos Hub automates policy distribution and synchronization across all PDPs using a push model. When a new policy bundle is available in your connected policy store (Git or another source), the Hub compiles it into a signed bundle and pushes it to every connected PDP. Each PDP stays in sync automatically without manual refresh or polling.
This approach eliminates version drift and ensures consistent authorization decisions everywhere. Cerbos Hub coordinates rollout across environments and supports on-prem, cloud, and hybrid deployments. Cerbos Hub shows which policies each PDP is serving, the exact bundle version, and when the instance was last seen.
The push model significantly reduces operational overhead and avoids the need for custom rollout scripts. It also provides visibility into policy versioning and rollout status.

Policy updates
With Cerbos PDP
Policy updates are made by editing the YAML files that define your authorization logic. These changes are stored on your end, and your own CI pipeline is responsible for validating the syntax, running tests, building a policy bundle, and publishing it to your policy store. This GitOps workflow gives you full control over how policies evolve over time, including change history and rollback.
However, you must maintain all of the supporting automation yourself. That includes writing CI jobs for validation, building bundles, handling test failures, and tracking which bundle version has been published. PDP instances simply consume whatever policy is available in the store. Coordinating when updates should be built, reviewed, or released is fully in your hands.
With Cerbos Hub
Cerbos Hub manages the full lifecycle of policy updates for you. When a policy is created or modified, the Hub validates it, runs tests, compiles a signed bundle, and marks it ready for deployment. You no longer need to maintain CI scripts, bundling logic, or custom tooling for policy publishing. Each update is versioned, reviewed, and auditable.

Decision and audit logs
With Cerbos PDP
Each PDP instance generates its own decision logs locally. If you run multiple PDPs, each one keeps its own log output, just like any other replicated microservice. PDPs do not provide a built-in way to combine logs from all instances or view authorization events in a single place.
These logs capture every authorization check, including the principal, action, resource, and decision result. By default, logs are written to standard output.
Forwarding logs to an external observability platform allows you to centralize storage and search, but this setup requires extra configuration and maintenance, and the volume of decision logs from fine-grained authorization may exceed the size and retention limits of those tools. These systems also store Cerbos logs as raw data, without built-in context about policy versions or decision lineage, so authorization analysis must be handled manually.
For small development environments, storing logs locally in each PDP may be sufficient. For distributed or compliance-driven systems, you will need either Cerbos Hub or a custom centralized logging solution to achieve full visibility and traceability.
With Cerbos Hub
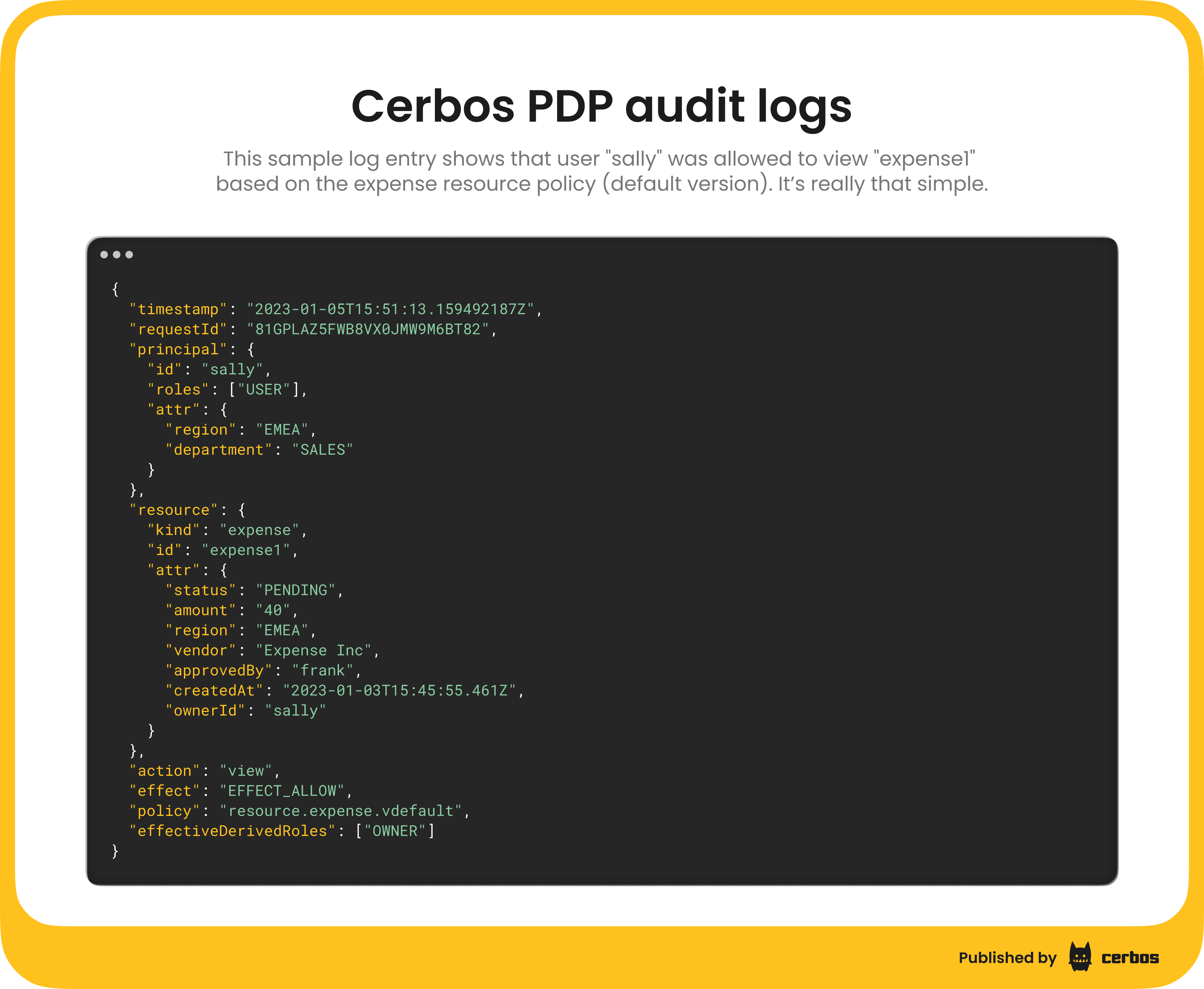
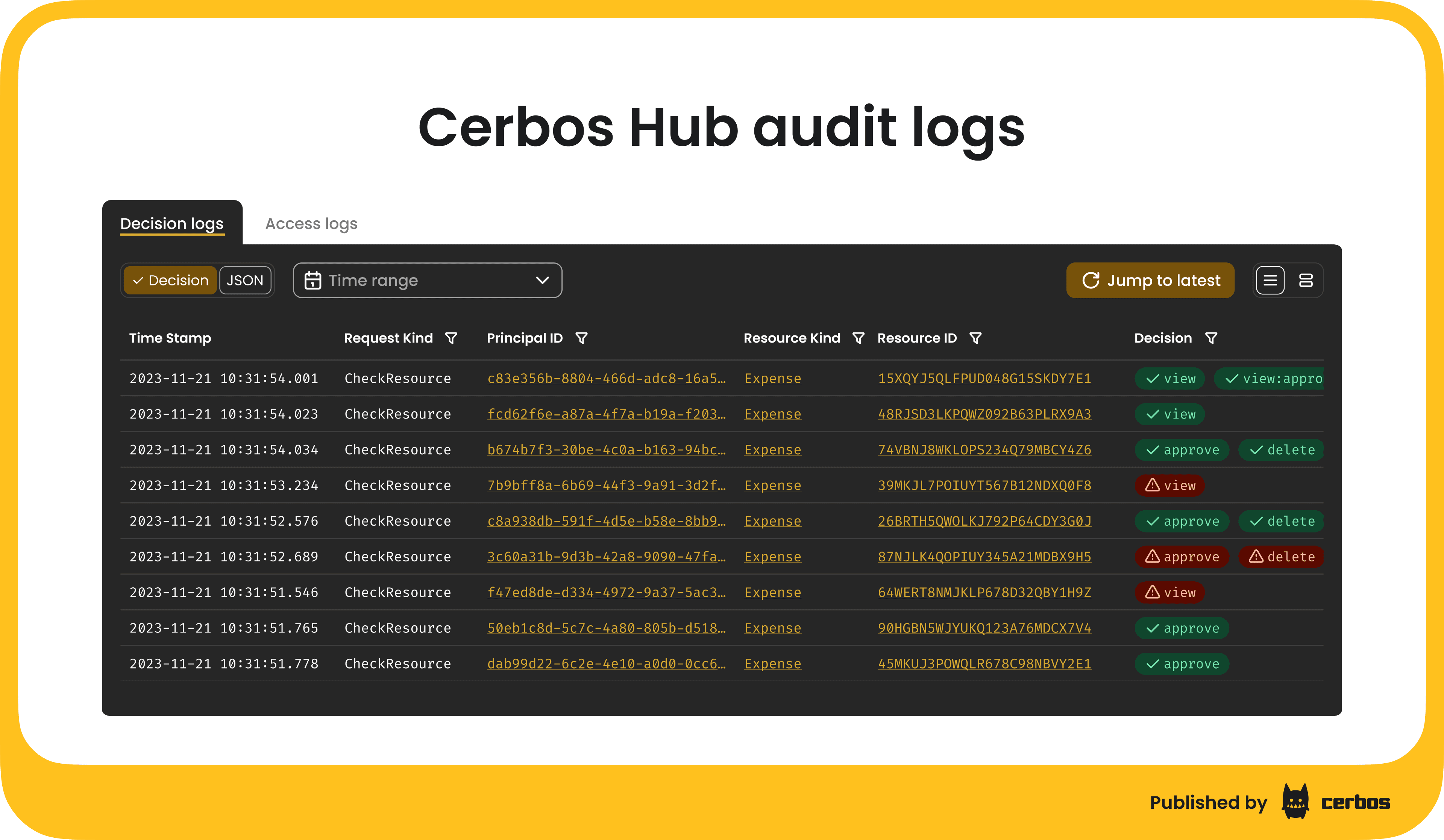
Cerbos Hub provides centralized audit log collection and visualization across all connected PDPs. Each PDP streams its decision logs to the Hub in real time, where they are indexed and searchable through a dedicated audit log interface.
You can view logs from all PDPs in one place, filter by attributes such as policy version or environment, and trace the exact policy that produced a given decision. This additional context is only possible to see in a single panel with Cerbos Hub, as it knows the policies that have been distributed, which PDPs are connected when, and ties the two data sets together in an authorization-specific workflow.
This model gives security and compliance teams complete visibility into authorization activity. They can investigate access patterns, confirm policy lineage, and maintain an audit trail across human, workload, and AI agent actions, all without building custom logging infrastructure.
Key learnings: what should you choose?
For proofs of concept or smaller products, the open source PDP can be more than enough. It gives you full control and flexibility when managing authorization locally.
For enterprise or large-scale systems with compliance, audit, or operational requirements, Cerbos Hub adds the automation and visibility needed to run authorization reliably at scale. It provides a managed environment for authoring, testing, and deploying policies, synchronizing PDPs, and monitoring access decisions across environments.
Choose Cerbos PDP together with Cerbos Hub when:
- You do not want to build or maintain authorization tooling yourself
- You need consistent policy management across multiple environments or regions
- You run many PDP instances and want automatic synchronization
- Compliance readiness is a requirement
- Reliable and low-latency policy updates matter
- Your team wants to get started quickly without a heavy setup

So, is it time to talk about ROI and costs? Beyond workflow improvements, you should also consider the engineering cost of building this functionality yourself. Everything that Cerbos Hub handles automatically must be built, integrated, and maintained if you rely only on the open source PDP. The table below shows the approximate investment required to reach feature parity:
| Capability | Included in Cerbos Hub | Engineering effort to build with PDP | Estimated cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| CI/CD for policies | Managed validation pipeline, rollouts, rollbacks | Write CI jobs, validation scripts, rollout playbooks | 6 FTE months |
| Testing & dev tooling | Playground IDE, API simulator, automated test runner | Build local test harnesses, fixtures, and CI test pipelines | 4 FTE months |
| Policy lifecycle management | Versioning, approval workflow, canary rollout, rollback | Implement versioning, release workflows, audit trails | 3 FTE months |
| Audit logs & visualization | Centralized audit UI, searchable logs, SIEM export, policy lineage | Stream logs, build ingestion pipelines, unify context, build UI | 6 FTE months |
When you add these pieces together, the cost and maintenance overhead become significant. Cerbos Hub exists to eliminate that burden. So your team can focus on shipping products instead of building internal authorization tooling.
P.S.: After all that detail, here is a more fun way to wrap up the article. This comic from our “Build vs Buy” guide says it all. 🙂

Book a free Policy Workshop to discuss your requirements and get your first policy written by the Cerbos team
Recommended content

Mapping business requirements to authorization policy
eBook: Zero Trust for AI, securing MCP servers

Experiment, learn, and prototype with Cerbos Playground
eBook: How to adopt externalized authorization

Framework for evaluating authorization providers and solutions

Staying compliant – What you need to know
Subscribe to our newsletter
Join thousands of developers | Features and updates | 1x per month | No spam, just goodies.
Authorization for AI systems
By industry
By business requirement
Useful links
What is Cerbos?
Cerbos is an end-to-end enterprise authorization software for Zero Trust environments and AI-powered systems. It enforces fine-grained, contextual, and continuous authorization across apps, APIs, AI agents, MCP servers, services, and workloads.
Cerbos consists of an open-source Policy Decision Point, Enforcement Point integrations, and a centrally managed Policy Administration Plane (Cerbos Hub) that coordinates unified policy-based authorization across your architecture. Enforce least privilege & maintain full visibility into access decisions with Cerbos authorization.
